Search Results for: Saturated fat

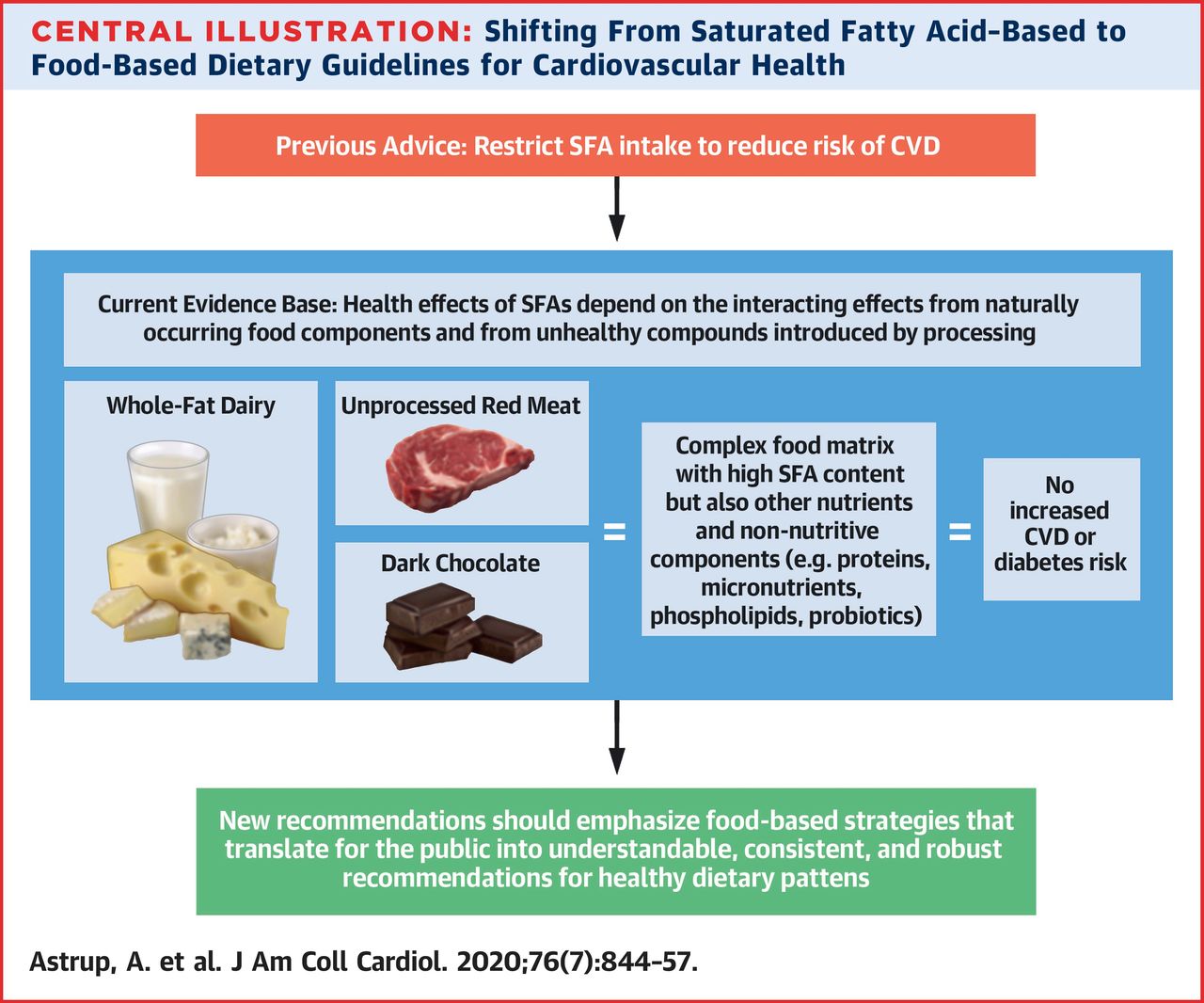
Saturated Fats and Health: AÂ Reassessment and Proposal for Food-Based Recommendations | JACC: Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Dave Asprey seems to do a good job at explaining what this study means:
“Something truly epic happened today that is going to change what you eat for years to come. Truly epic. The Journal of the American College of cardiology published a groundbreaking paper today admitting something that you already knew if you had been on the Bulletproof Diet for the last 10 years. (Yes, I am feeling slightly vindicated after receiving so much resistance after writing The Bulletproof Diet, which eventually helped people lose about 1,000,000 pounds!)This new paper, which uses data from studying 135,000 people overtime, finds:-Saturated fat from meat and dairy do not cause an increase in cardiovascular disease, and reduce stroke risk.-Polyunsaturated fats increase risk of cardiovascular disease.-Different fats do different things-Cutting saturated fat does not reduce death rate-the 25% of people eating the highest saturated fat intake (about ∼14% of calories) had lower risk of stroke-Only 5% of fat should be polyunsaturated for lowest death. This is effectively a deathblow to vegan and plant-based practices, which make people sick over time because they contain almost all polyunsaturated fats. It’s one reason I got sicker when I was a vegan. (It takes 2 years to replace half your cell membrane fats when you change your diet.)”

Western high-fat diet can cause chronic pain, according to new study — ScienceDaily
In the new paper, Dr. Boyd and his colleagues used multiple methods in both mice and humans to study the role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in pain conditions. They found that typical Western diets high in omega-6 polyunsaturated fats served as a significant risk factor for both inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/06/210623141644.htm

An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity
” In the past three decades, total fat and saturated fat intake as a percentage of total calories has continuously decreased in Western diets, while the intake of omega-6 fatty acid increased and the omega-3 fatty acid decreased, resulting in a large increase in the omega-6/omega-3 ratio from 1:1 during evolution to 20:1 today or even higher. This change in the composition of fatty acids parallels a significant increase in the prevalence of overweight and obesity. Experimental studies have suggested that omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids elicit divergent effects on body fat gain through mechanisms of adipogenesis, browning of adipose tissue, lipid homeostasis, brain-gut-adipose tissue axis, and most importantly systemic inflammation. Prospective studies clearly show an increase in the risk of obesity as the level of omega-6 fatty acids and the omega-6/omega-3 ratio increase in red blood cell (RBC) membrane phospholipids, whereas high omega-3 RBC membrane phospholipids decrease the risk of obesity. Recent studies in humans show that in addition to absolute amounts of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acid intake, the omega-6/omega-3 ratio plays an important role in increasing the development of obesity via both AA eicosanoid metabolites and hyperactivity of the cannabinoid system, which can be reversed with increased intake of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). A balanced omega-6/omega-3 ratio is important for health and in the prevention and management of obesity. ”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808858/

The Potential Influence of the Bacterial Microbiome on the Development and Progression of ADHD
The latest research cumulates staggering information about the correlation between the microbiota-gut-brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. This review aims to shed light on the potential influence of the microbiome on the development of the most prevalent neurodevelopmental disease, attention-deficit-hyperactive disorder (ADHD). As the etiology and pathophysiology of ADHD are still unclear, finding viable biomarkers and effective treatment still represent a challenge. Therefore, we focused on factors that have been associated with a higher risk of developing ADHD, while simultaneously influencing the microbial composition. We reviewed the effect of a differing microbial makeup on neurotransmitter concentrations important in the pathophysiology of ADHD. Additionally, we deduced factors that correlate with a high prevalence of ADHD, while simultaneously affecting the gut microbiome, such as emergency c-sections, and premature birth as the former leads to a decrease of the gut microbial diversity and the latter causes neuroprotective Lactobacillus levels to be reduced. Also, we assessed nutritional influences, such as breastfeeding, ingestion of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) on the host?s microbiome and development of ADHD. Finally, we discussed the potential significance of Bifidobacterium as a biomarker for ADHD, the importance of preventing premature birth as prophylaxis and nutrition as a prospective therapeutic measurement against ADHD.

You don’t have to go cold turkey on red meat to see health benefits — ScienceDaily
A new study has found that halving the amount red and processed (RPM) meat in the diet can have a significant impact on health, reducing the amount of LDL ‘bad’ cholesterol in the blood which cuts the risk of developing heart disease. Red and processed meat (RPM) include fresh pork, beef, lamb and veal and meats that have been smoked, cured or preserved (other than freezing) in some way. These meats are typically high in saturated fatty acids which cause an increase in LDL cholesterol. This is the “bad” cholesterol that collects in the walls of blood vessels, where it can cause blockages and raise the chance of a heart attack. Increasing awareness of the risks associated with eating red and processed meat has led to a growing number of people adopting vegetarian and vegan diets, which cut out meat completely. Researchers at the University of Nottingham wanted to find out if reducing the amount of red meat eaten, rather than cutting it out completely, would have a positive effect on the health of the subjects taking part.
You don’t have to go cold turkey on red meat to see health benefits — ScienceDaily