Category: Uncategorized


Accelerated biological aging in COVID-19 patients | Nature Communications
Chronological age is a risk factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19. Previous findings indicate that epigenetic age could be altered in viral infection. However, the epigenetic aging in COVID-19 has not been well studied. In this study, DNA methylation of the blood samples from 232 healthy individuals and 413 COVID-19 patients is profiled using EPIC methylation array. Epigenetic ages of each individual are determined by applying epigenetic clocks and telomere length estimator to the methylation profile of the individual.

Mullets for Mental Health – Health Hackers
Science. Compassion. Action.
We’re all ears for Black Dog Institute’s Mullets for Mental Health.
1 in 5 of us will experience symptoms of mental illness in any given year. In Australia that’s around 5 million people. And roughly 65% of these people won’t seek help.
For the month of September we will be sporting mullets and raising funds to show support for mental health research.
Please donate and support our mullets and empower everyone in Australia to look after their mental health.
https://www.mulletsformentalhealth.org.au/fundraisers/healthhackers

MMA Summit

Fasting and Exercise Induce Changes in Serum Vitamin D Metabolites in Healthy Men
Increases in 24,25(OH)2D3 and 3-epi-25(OH)D3 levels imply that fasting stimulates vitamin D metabolism. The effects of exercise on serum vitamin D metabolites, which are most pronounced after fasting and in subjects with serum 25(OH)D3 above 25 ng/mL, support the notion that fasting and exercise augment vitamin D metabolism.

Frontiers | The Effects of Daytime Psilocybin Administration on Sleep: Implications for Antidepressant Action | Pharmacology
Psilocybin (O-phosphoryl-4hydroxy-N, N-dimethyltryptamine) and its active metabolite psilocin (4-hydroxy-N, N-dimethyltryptamine) are the main psychoactive components of psychedelic mushrooms. In the central nervous system, psilocin acts as an agonist of serotonergic 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/C receptors, leading to altered states of consciousness in humans (Tyls et al., 2014). Psilocybin doses of 0.04–0.43 mg/kg cause alterations in perception, cognition, and emotions, while also eliciting long-term changes in well-being and mood in both healthy and psychiatric subjects (Dos Santos et al., 2016; Kor?ák et al., 2019; Barrett et al., 2020). These long-lasting positive changes lead to an exploration of the therapeutic potential of psychedelics as well as the mechanisms underlying this potential. Because of its general safety, intermediate duration of action, and therapeutic potential in several neuropsychiatric disorders, psilocybin is currently the most intensely studied psychedelic in clinical trials (Sewell et al., 2006; Grob et al., 2011; Stebelska, 2013; Dos Santos, 2014).
Overall, there has been an increasing preclinical (Catlow et al., 2013; Baumeister et al., 2014) and clinical (Carhart-Harris et al., 2016; Bogenschutz and Ross, 2018) evidence for the antidepressant potential of psilocybin. Although exact mechanisms are currently unknown, it is generally believed to be attributed to either a direct action on 5-HT receptors or the psychological effects of acute intoxication (Carhart-Harris and Goodwin, 2017). It has been shown that serotonergic psychedelics including psilocybin via 5-HT2A receptors promote neuroplasticity (Ly et al., 2018), a fundamental mechanism of neuronal adaptation that is disrupted in depression (Carhart-Harris and Goodwin, 2017) and restored by antidepressant treatments including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) (Hayley and Littlejohn, 2013).
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.602590/full

Associations between fruit intake and risk of diabetes in the AusDiab cohort – PubMed
A healthy diet including whole fruits, but not fruit juice, may play a role in mitigating T2DM risk.
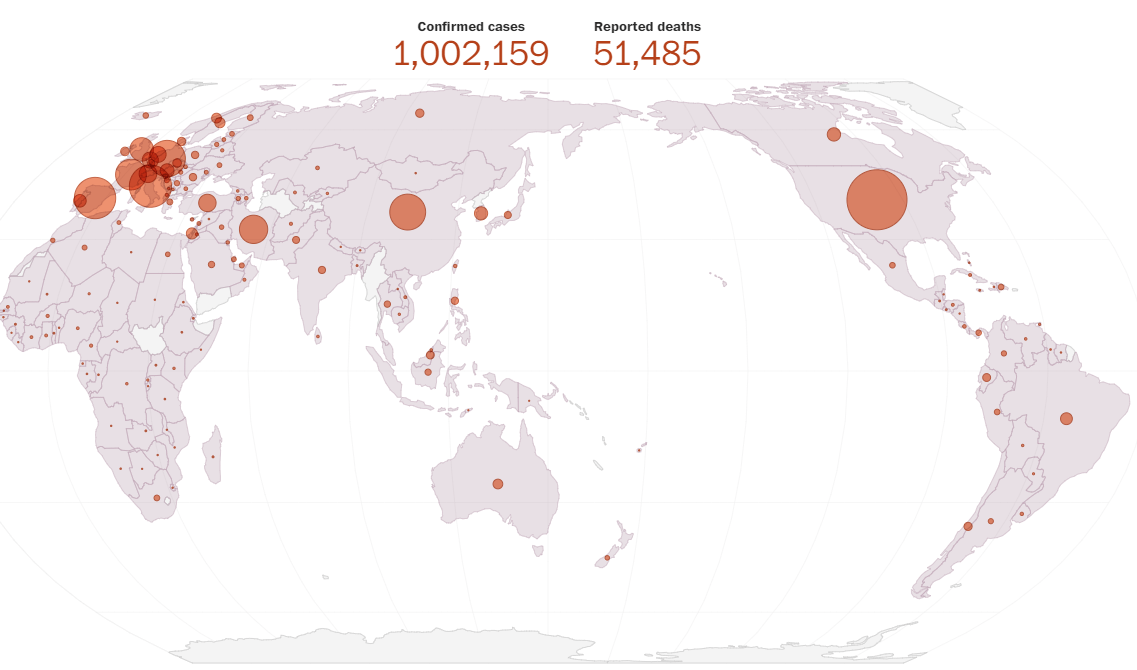
Part 1: My COVID-19 update – April 1st – Dr David A Sinclair
“It’s April 1st, 2020. If only the headlines were a joke. Our nation’s leaders will soon be faced with a difficult choice. Hunker down for another four months and wreck the economy or let people out in two months and kill an additional hundred thousand people.
Professor Samir Bhatt, Senior Lecturer at the Imperial College of London, and his colleagues calculate that, globally, up to 43 million people have been infected with SARS-CoV-2. They predict that if we’d gone about our normal lives, COVID-19 would have caused 7 billion infections and 40 million deaths this year. Shielding only the elderly may have halved the number of deaths, a strategy the UK initially entertained, but health systems would have been overwhelmed, so that tactic was largely abandoned.
Based on the advice of professional epidemiologists, most nations have adopted a stretch-it-out and hope it doesn’t return strategy. It seems to be working so far. Rates of new cases are declining in Europe and the US. If the current suppression strategies are sustained, then 38.7 million lives globally will be saved this year, the epidemiologists at the Imperial College calculate.
But epidemiologists aren’t economists. We can not stay home for the rest of the year – the economic impact would be too high. We are three weeks into the shutdown and already factories are ceasing production, brick-and-mortar retail stores and restaurants are closed, unemployment spikes are unprecedented, commodity prices have plunged, and a wave of loan defaults is expected.
A colleague on a global pandemic response panel tells me the panel’s best estimate is that the US economy will rebound rapidly, but only if the nation returns to work in 60 days. After that, it’s anyone’s guess. No one, not even the experts, are willing to estimate the full economic impact of COVID-19. It will depend on how long it takes to get back to work and how many times we will be sent back home.”
https://mailchi.mp/lifespanbook.com/my-covid-19-update-2572786

ACMA to set EME standards for mmWave 5G devices
“The Australian Communications and Media Authority is looking at how it can regulate electromagnetic energy (EME) exposure from 5G devices operating in millimetre-wave (mmWave) frequencies.”
ACMA to set EME standards for mmWave 5G devices – Telco/ISP – iTnews

Update: Australian Bushfire appeal reaches almost $25m
Aussie comedian raises almost $25m for Aussie fire service with Facebook donation platform.
If you wish to contribute you can Donate here

Effects of dairy consumption on SIRT1 and mitochondrial biogenesis in adipocytes and muscle cells. – PubMed – NCBI
“These data indicate that dairy consumption leads to systemic effects, which may promote mitochondrial biogenesis in key target tissues such as muscle and adipose tissue both by direct activation of SIRT1 as well as by SIRT1-independent pathways.”
Notice the word dairy is used, not milk. see our previous post on milkand its mTor activation and AMPK suppression.

Which companies are working on longevity?
http://agingbiotech.info/companies/

Key concepts for making informed choices
This is not related to the subject of this blog however, it is a major focus of this blog to present only trustworthy information and to do so we apply some critical thinking to any sources we post here. We suggest everyone do the same.

Alternate day fasting combined with high protien/low carb diet
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31224368

The gut microbiota regulates white adipose tissue inflammation and obesity via a family of microRNAs
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31218777

Alcohol causes most overall harm of any drug, says study
It also directly kills NAD+ so Alcohol makes you age!
https://www.msn.com/en-au/health/medical/alcohol-causes-most-overall-harm-of-any-drug-says-study/ar-AADgpwY?ocid=anaheimntp

Cannabidiol-loaded microspheres incorporated into osteoconductive scaffold enhance mesenchymal stem cell recruitment and regeneration of critical-s… – PubMed – NCBI
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Aug;101:64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.03.070. Epub 2019 Mar 24.