Author: NathanRead my blog or one of my many profiles lol


Fasting and Exercise Induce Changes in Serum Vitamin D Metabolites in Healthy Men
Increases in 24,25(OH)2D3 and 3-epi-25(OH)D3 levels imply that fasting stimulates vitamin D metabolism. The effects of exercise on serum vitamin D metabolites, which are most pronounced after fasting and in subjects with serum 25(OH)D3 above 25 ng/mL, support the notion that fasting and exercise augment vitamin D metabolism.

Frontiers | The Effects of Daytime Psilocybin Administration on Sleep: Implications for Antidepressant Action | Pharmacology
Psilocybin (O-phosphoryl-4hydroxy-N, N-dimethyltryptamine) and its active metabolite psilocin (4-hydroxy-N, N-dimethyltryptamine) are the main psychoactive components of psychedelic mushrooms. In the central nervous system, psilocin acts as an agonist of serotonergic 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/C receptors, leading to altered states of consciousness in humans (Tyls et al., 2014). Psilocybin doses of 0.04–0.43 mg/kg cause alterations in perception, cognition, and emotions, while also eliciting long-term changes in well-being and mood in both healthy and psychiatric subjects (Dos Santos et al., 2016; Kor?ák et al., 2019; Barrett et al., 2020). These long-lasting positive changes lead to an exploration of the therapeutic potential of psychedelics as well as the mechanisms underlying this potential. Because of its general safety, intermediate duration of action, and therapeutic potential in several neuropsychiatric disorders, psilocybin is currently the most intensely studied psychedelic in clinical trials (Sewell et al., 2006; Grob et al., 2011; Stebelska, 2013; Dos Santos, 2014).
Overall, there has been an increasing preclinical (Catlow et al., 2013; Baumeister et al., 2014) and clinical (Carhart-Harris et al., 2016; Bogenschutz and Ross, 2018) evidence for the antidepressant potential of psilocybin. Although exact mechanisms are currently unknown, it is generally believed to be attributed to either a direct action on 5-HT receptors or the psychological effects of acute intoxication (Carhart-Harris and Goodwin, 2017). It has been shown that serotonergic psychedelics including psilocybin via 5-HT2A receptors promote neuroplasticity (Ly et al., 2018), a fundamental mechanism of neuronal adaptation that is disrupted in depression (Carhart-Harris and Goodwin, 2017) and restored by antidepressant treatments including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) (Hayley and Littlejohn, 2013).
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.602590/full

Victorian breakthrough in cannabis DNA
https://youtu.be/Ntz2cUnonTk

Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Effects of L-Theanine Administration on Stress-Related Symptoms and Cognitive Functions in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Our findings suggest that L-theanine has the potential to promote mental health in the general population with stress-related ailments and cognitive impairments.

BrainNet: A Multi-Person Brain-to-Brain Interface for Direct Collaboration Between Brains
We present BrainNet which, to our knowledge, is the first multi-person non-invasive direct brain-to-brain interface for collaborative problem solving. The interface combines electroencephalography (EEG) to record brain signals and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to deliver information noninvasively to the brain.

Research News – Success in Reversing Dementia in Mice Sets the Stage for Human Clinical Trials | Tohoku University Global Site
Researchers have identified a new treatment candidate that appears to not only halt neurodegenerative symptoms in mouse models of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but also reverse the effects of the disorders.
https://www.tohoku.ac.jp/en/press/eversing_dementia_stage_set_for_human_clinical_trials.html

The terrible science behind popular weight loss products
Dietary supplements and alternative therapies for weight loss have a limited high-quality evidence base of efficacy. Practitioners and patients should be aware of the scientific evidence of claims before recommending use.
https://www.inverse.com/mind-body/new-study-debunks-weight-loss-supplements

Running to music combats mental fatigue, study suggests — ScienceDaily
Listening to music while running might be the key to improving people’s performance when they feel mentally fatigued a study suggests. The performance of runners who listened to a self-selected playlist after completing a demanding thinking task was at the same level as when they were not mentally fatigued, the research found. The study is the first to investigate the effect of listening to music playlists on endurance running capacity and performance when mentally fatigued.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/06/210622123235.htm

Western high-fat diet can cause chronic pain, according to new study — ScienceDaily
In the new paper, Dr. Boyd and his colleagues used multiple methods in both mice and humans to study the role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in pain conditions. They found that typical Western diets high in omega-6 polyunsaturated fats served as a significant risk factor for both inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/06/210623141644.htm

Evidence for Clinical Use of Honey in Wound Healing as an Anti-bacterial, Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidant and Anti-viral Agent: A Review
Honey has almost equal or slightly superior effects when compared with conventional treatments for acute wounds and superficial partial thickness burns.

Study: Men doing more family caregiving could lower their risk of suicide | EurekAlert! Science News
Men’s family caregiving, unemployment, and suicide
The multinational and multidisciplinary study, published in Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology by Canetto, Ying-Yeh Chen, ZiYi Cai, Qingsong Chang, and Paul Yip, offers evidence of a suicide-protective role for men who engage in family caregiving. In their study, family caregiving was defined as, for example, providing personal care or education for a child, and/or providing care for a dependent adult.
The researchers examined suicide, male family caregiving, and unemployment in 20 countries, including the United States, Austria, Belgium, Canada and Japan. Suicide rates were found to be lower in countries where men reported more family care work.
In countries where men reported more such care work, higher unemployment rates were not associated with higher suicide rates in men. By contrast, in countries where men reported less family care work, higher unemployment rates were associated with elevated male suicide rates. Incidentally, unemployment benefits did not reduce male suicide rates.
Taken together, the findings of this ecological study suggest that men’s family care work may protect them against suicide, particularly under difficult economic circumstances, Canetto said.
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2021-06/csu-smd061821.php

A catalog of tens of thousands of viruses from human metagenomes reveals hidden associations with chronic diseases | PNAS
The microbiome, an important regulator of metabolic and immune-related phenotypes, has been shown to be associated with or participate in the development of a variety of chronic diseases. Viruses of bacteria (i.e., “phages”) are ubiquitous and mysterious, and several studies have shown that phages exert great control over the behavior—and misbehavior—of their host bacteria.

Associations between fruit intake and risk of diabetes in the AusDiab cohort – PubMed
A healthy diet including whole fruits, but not fruit juice, may play a role in mitigating T2DM risk.

View of Hair Regrowth with Cannabidiol (CBD)-rich Hemp Extract
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common cause of hair loss. Several FDA approved medications are available
but offer limited results. Studies have shown that the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a key player in hair follicle
cell growth. The ECS can
nabinoid type one (CB1) receptors are well expressed in the hair follicle cells. Cannabidiol
CBD is a negative allosteric modulator of the CB1 receptor and has been shown to result in hair shaft elongation. In
addition, the hair follicle cycle phases are c
ontrolled by the ECS vanilloid receptor
–
1 (TRPV1). CBD has also been
shown to increase Wnt signaling pathways that are involved in the differentiation of dermal progenitor cells into new
hair follicles and maintaining the anagen phase of the hair cycle. Th
e effects of CBD on hair growth are dose
dependent and higher doses may result in premature entry into the catagen phase via a receptor known as vanilloid
receptor
–
4 (TRPV4). Topical application of CBD reaches hair follicles where it is a CB1 negative modu
lator, and
TRPV1, and TRPV4 agonist. A study was done of 35 subjects with AGA using a once daily topical hemp oil
formulation, averaging about 3
–
4 mg per day of CBD and minimal amounts of other cannabinoids for six months. A
hair count of the greatest area
of alopecia was carried out before treatment and again after six months. The results
revealed that men did slightly better than women, and the vertex area did better than the temporal areas. On
average there was statistically significant 93.5% increase in
hair after 6 months. All subjects had some regrowth.
There were no reported adverse effects. Since the CBD works through novel mechanisms different from finasteride
and minoxidil it can be used in conjunction with these current drugs and would be expected
to have synergistic
effects.
https://publications.sciences.ucf.edu/cannabis/index.php/Cannabis/article/view/78/47

There Is No Evidence That Associations Between Adolescents’ Digital Technology Engagement and Mental Health Problems Have Increased – Matti Vuorre, Amy Orben, Andrew K. Przybylski, 2021
And this was a warning to regulators and lawmakers focusing on commonly held beliefs about the harmful effects of technology on young people’s mental health.
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2167702621994549

Pain receptors linked to the generation of energy-burning brown fat cells: Vascular smooth muscle-derived Trpv1+ progenitors have found to be a source of cold-induced — ScienceDaily
A new source of energy expending brown fat cells has been uncovered by researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center, which they say points towards potential new therapeutic options for obesity. According to the new report, published in Nature Metabolism on 12 March 2021, the key lies in the expression of a receptor called Trpv1 (temperature-sensitive ion channel transient receptor potential cation subfamily V member 1) — a protein known to sense noxious stimuli, including pain and temperature.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/04/210412114837.htm

COVID-19 pandemic has been linked with six unhealthy eating behaviors: Study shows a slight increase in eating disorders, one of the deadliest psychiatric health concerns — ScienceDaily
Eat healthy:
A new probe into the lingering impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic revealed correlations to six unhealthy eating behaviors, according to a study by the University of Minnesota Medical School and School of Public Health. Researchers say the most concerning finding indicates a slight increase or the re-emergence of eating disorders, which kill roughly 10,200 people every year — about one person every 52 minutes.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/04/210412114740.htm

CBD reduces plaque, improves cognition in model of familial Alzheimer’s – Jagwire
The investigators report for the first time that CBD normalizes levels and function, improving cognition as it also reduces levels of the immune protein IL-6, which is associated with the high inflammation levels found in Alzheimer’s, says Dr. Babak Baban, immunologist and associate dean for research in the Dental College of Georgia and the study’s corresponding author.
https://jagwire.augusta.edu/cbd-reduces-plaque-improves-cognition-in-model-of-familial-alzheimers/

Study compares low-fat, plant-based diet to low-carb, animal-based diet
People on a low-fat, plant-based diet ate fewer daily calories but had higher insulin and blood glucose levels, compared to when they ate a low-carbohydrate, animal-based diet, according to a small but highly controlled study. The study compared the effects of the two diets on calorie intake, hormone levels, body weight, and more.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/01/210121131851.htm

Brain imaging reveals ADHD as a collection of different disorders — ScienceDaily
Researchers have found that patients with different types of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have impairments in unique brain systems, indicating that there may not be a one-size-fits-all explanation for the cause of the disorder. Based on performance on behavioral tests, adolescents with ADHD fit into one of three subgroups, where each group demonstrated distinct impairments in the brain with no common abnormalities between them.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/11/171107140834.htm

Exercising one arm has twice the benefits — ScienceDaily
New research has revealed that training one arm can improve strength and decrease muscle loss in the other arm — without even moving it. The findings could help to address the muscle wastage and loss of strength often experienced in an immobilized arm, such as after injury, by using eccentric exercise on the opposing arm.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/10/201022112555.htm

Study probes connection between diet quality and environmental sustainability | William & Mary
While a plant based diet may seem to have good environmental credentials, it isn’t necessarily better for the environment.
A plant based diet is also deficient and requires close attention and supplementation.

Exercise and nutrition regimen benefits physical, cognitive health: 12-week double-blind control trial in 148 Air Force airmen — ScienceDaily
“Researchers studied the effects of a 12-week exercise regimen on 148 active-duty Air Force airmen, half of whom also received a twice-daily nutrient beverage that included protein; the omega-3 fatty acid, DHA; lutein; phospholipids; vitamin D; B vitamins and other micronutrients; along with a muscle-promoting compound known as HMB. Both groups improved in physical and cognitive function, with added gains among those who regularly consumed the nutritional beverage, the team reports.”
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/10/201019103508.htm

Health and disease markers correlate with gut microbiome composition across thousands of people | Nature Communications
“We identify major axes of taxonomic variance in the gut and a putative diversity maximum along the Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes axis. Our analyses reveal both known and unknown associations between microbiome composition and host clinical markers and lifestyle factors, including host-microbe associations that are composition-specific. These results suggest potential opportunities for targeted interventions that alter the composition of the microbiome to improve host health.”

TREATMENT OF AGE-RELATED AND MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASES BY INHIBITION OF HIF-1 ALPHA FUNCTION – President and Fellows of Harvard College
Following we have a new patent application from Dr. David Sinclair et al
It describes the use of NMN on humans and dosage rates.

Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research study finds honeybee venom rapidly kills aggressive breast cancer cells – ABC News
”
Venom from honeybees has been found to rapidly kill aggressive and hard-to-treat breast cancer cells, according to potentially groundbreaking new Australian research.
Key points:
- The research was published in the journal Nature Precision Oncology
- It found honeybee venom was effective in killing breast cancer cells
- Researchers say the discovery is exciting but there is a long way to go”

Massive Study of 24,000 Dreams Suggests They Really Are Continuations of Reality
“
“Research has repeatedly provided strong support for what sleep scientists refer to as the ‘continuity hypothesis of dreams‘: most dreams are a continuation of what is happening in everyday life,” researchers led by computer scientist Alessandro Fogli from Roma Tre University in Italy explain in a new study.
“It turns out that everyday life impacts dreaming (e.g. anxiety in life leads to dreams with negative affect) and vice versa (e.g. dreaming impacts problem-solving skills).”
These psychological theories date back to the work of Sigmund Freud and others in the 20th century, who spearheaded the notion that the hidden meanings of dreams could be unlocked when examined within the context of a person’s real-world experiences.”

Effects of oily fish intake on cognitive and socioemotional function in healthy 8–9-year-old children: the FiSK Junior randomized trial | The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | Oxford Academic
“Oily fish dose-dependently improved cognitive function, especially attention and cognitive flexibility, and reduced socioemotional problems. The results support the importance of n–3 LCPUFAs for optimal brain function and fish intake recommendations in children.”
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/112/1/74/5855515?searchresult=1

Effects of oily fish intake on cognitive and socioemotional function in healthy 8–9-year-old children: the FiSK Junior randomized trial | The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | Oxford Academic
“Oily fish dose-dependently improved cognitive function, especially attention and cognitive flexibility, and reduced socioemotional problems. The results support the importance of n–3 LCPUFAs for optimal brain function and fish intake recommendations in children.”
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/112/1/74/5855515?searchresult=1
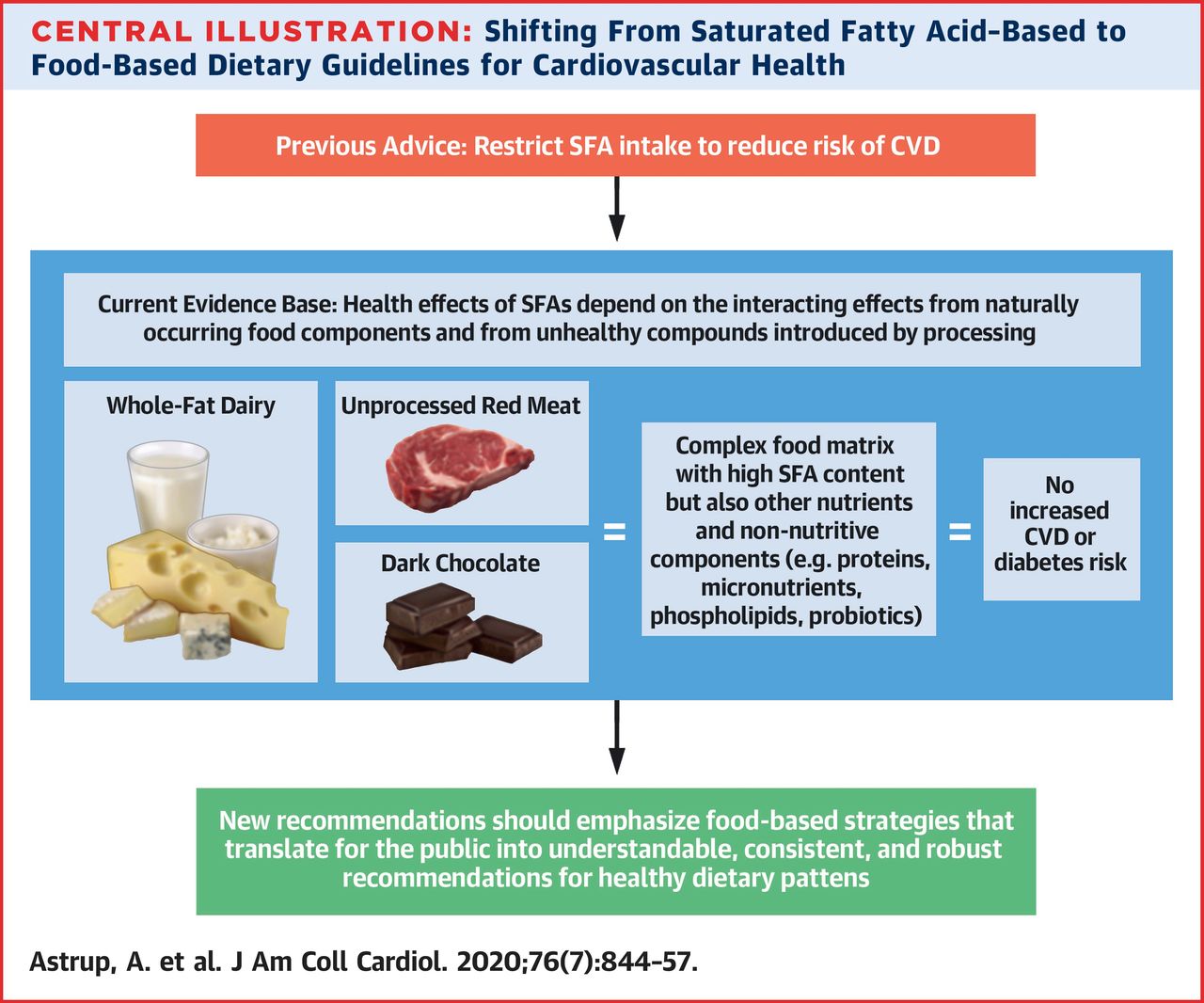
Saturated Fats and Health: AÂ Reassessment and Proposal for Food-Based Recommendations | JACC: Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Dave Asprey seems to do a good job at explaining what this study means:
“Something truly epic happened today that is going to change what you eat for years to come. Truly epic. The Journal of the American College of cardiology published a groundbreaking paper today admitting something that you already knew if you had been on the Bulletproof Diet for the last 10 years. (Yes, I am feeling slightly vindicated after receiving so much resistance after writing The Bulletproof Diet, which eventually helped people lose about 1,000,000 pounds!)This new paper, which uses data from studying 135,000 people overtime, finds:-Saturated fat from meat and dairy do not cause an increase in cardiovascular disease, and reduce stroke risk.-Polyunsaturated fats increase risk of cardiovascular disease.-Different fats do different things-Cutting saturated fat does not reduce death rate-the 25% of people eating the highest saturated fat intake (about ∼14% of calories) had lower risk of stroke-Only 5% of fat should be polyunsaturated for lowest death. This is effectively a deathblow to vegan and plant-based practices, which make people sick over time because they contain almost all polyunsaturated fats. It’s one reason I got sicker when I was a vegan. (It takes 2 years to replace half your cell membrane fats when you change your diet.)”

Scientists inspired by ‘Star Wars’ create artificial skin able to feel – Reuters
SINGAPORE (Reuters) – Singapore researchers have developed “electronic skin†capable of recreating a sense of touch, an innovation they hope will allow people with prosthetic limbs to detect objects, as well as feel texture, or even temperature and pain.
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-singapore-skin-idUSKBN24Z13D

Scientists inspired by ‘Star Wars’ create artificial skin able to feel – Reuters
SINGAPORE (Reuters) – Singapore researchers have developed “electronic skin†capable of recreating a sense of touch, an innovation they hope will allow people with prosthetic limbs to detect objects, as well as feel texture, or even temperature and pain.
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-singapore-skin-idUSKBN24Z13D

Niacin Increases NAD+ Significantly in Human Trial | Lifespan.io
The results of a new human trial using niacin shed new light on its role in NAD+ biology [1].
The trial participants were given a steadily increasing dose of niacin, starting at 250 mg/day to 750-1000 mg/day over a 4-month period, then a 10-month follow-up treatment period. The participants were organized into a study group of individuals with mitochondrial myopathy and a control group of healthy age-matched people consisting of two healthy people for each patient with mitochondrial myopathy. All the study participants were placed on the same niacin supplementation regimen.
The researchers report that niacin treatment increased muscle NAD+ levels by 1.3-fold at 4 months and 2.3-fold after 10 months in the study group.
https://www.lifespan.io/news/niacin-increases-nad-significantly-in-human-trial/

Niacin Increases NAD+ Significantly in Human Trial | Lifespan.io
The results of a new human trial using niacin shed new light on its role in NAD+ biology [1].
The trial participants were given a steadily increasing dose of niacin, starting at 250 mg/day to 750-1000 mg/day over a 4-month period, then a 10-month follow-up treatment period. The participants were organized into a study group of individuals with mitochondrial myopathy and a control group of healthy age-matched people consisting of two healthy people for each patient with mitochondrial myopathy. All the study participants were placed on the same niacin supplementation regimen.
The researchers report that niacin treatment increased muscle NAD+ levels by 1.3-fold at 4 months and 2.3-fold after 10 months in the study group.
https://www.lifespan.io/news/niacin-increases-nad-significantly-in-human-trial/

Niacin Increases NAD+ Significantly in Human Trial | Lifespan.io
The results of a new human trial using niacin shed new light on its role in NAD+ biology [1].
The trial participants were given a steadily increasing dose of niacin, starting at 250 mg/day to 750-1000 mg/day over a 4-month period, then a 10-month follow-up treatment period. The participants were organized into a study group of individuals with mitochondrial myopathy and a control group of healthy age-matched people consisting of two healthy people for each patient with mitochondrial myopathy. All the study participants were placed on the same niacin supplementation regimen.
The researchers report that niacin treatment increased muscle NAD+ levels by 1.3-fold at 4 months and 2.3-fold after 10 months in the study group.
https://www.lifespan.io/news/niacin-increases-nad-significantly-in-human-trial/

Diluting blood plasma rejuvenates tissue and reverses aging – Neuroscience News
Summary: Diluting the blood plasma of older mice has a stronger rejuvenating effect on the brain, liver, and muscles than transplanting the blood of younger mice.
Source: UC Berkeley
In 2005, University of California, Berkeley, researchers made the surprising discovery that making conjoined twins out of young and old mice — such that they share blood and organs — can rejuvenate tissues and reverse the signs of aging in the old mice. The finding sparked a flurry of research into whether a youngster’s blood might contain special proteins or molecules that could serve as a “fountain of youth†for mice and humans alike.
But a new study by the same team shows that similar age-reversing effects can be achieved by simply diluting the blood plasma of old mice — no young blood needed.

Why are the elderly more affected by COVID-19? – YouTube

Australian-made wearable biosensors to gather precision data on chronic disease – Hardware – iTnews
Melbourne-based company Nutromics is developing the alternative to painful finger pricks and blood tests to measure key dietary biomarkers in real time.
Australian-made wearable biosensors to gather precision data on chronic disease – Hardware – iTnews
Consumer trends during Covid-19
Some interesting and somewhat encouraging news from the Woolworths CEO today via his email updates during Covid-19 show some interesting trends in consumer spending on food and vitamins during this time.
To quote from his email:
“We are becoming healthier and more adventurous in our cooking
While the slow cooking movement continues, we’re also becoming increasingly adventurous. Ingredients such as cardamom, saffron and dried sesame seeds have doubled in sales. Roasted peppers are up 65%, Asian and hot chilli sauces are both up 40% and capers are up 35%.
We’re also well into soup season. What’s interesting this year is the explosive growth of dried soup mix packets (up 200%) as people make more warming soup at home.
It’s also interesting to see customers think about their health, with a big rise in vitamin sales, plus ground ginger and turmeric sales up 120% and sauerkraut up 76%. On a related topic, sales of cough and cold products are much lower this year compared to last year.”
This is encouraging and hopefully a sign that the general population is starting to become more interested in preparing fresh meals rather than fast food, and hopefully the rise in vitamins and other beneficial products is a sign that people are starting to see value in improving their health and eating better.
It’s pretty clear that the more fit and healthy you are and the better you eat, the less likely you are to contract Covid-19 and, less likely to have severe complication if you do. We have been keeping an eye on developments and have been hoping that the silver lining from all of this may be a new focus on health and well-being.
So please ensure you take some time out of your busy life to focus on whats really important, your life! We at Health Hacker wish all of you good health and encourage you to keep exploring and trying to improve your diet and lifestyle as much as possoble. Remember, something is better than nothing so start on somethign today!
Part 1: My COVID-19 update – April 1st – Dr David A Sinclair
“It’s April 1st, 2020. If only the headlines were a joke. Our nation’s leaders will soon be faced with a difficult choice. Hunker down for another four months and wreck the economy or let people out in two months and kill an additional hundred thousand people.
Professor Samir Bhatt, Senior Lecturer at the Imperial College of London, and his colleagues calculate that, globally, up to 43 million people have been infected with SARS-CoV-2. They predict that if we’d gone about our normal lives, COVID-19 would have caused 7 billion infections and 40 million deaths this year. Shielding only the elderly may have halved the number of deaths, a strategy the UK initially entertained, but health systems would have been overwhelmed, so that tactic was largely abandoned.
Based on the advice of professional epidemiologists, most nations have adopted a stretch-it-out and hope it doesn’t return strategy. It seems to be working so far. Rates of new cases are declining in Europe and the US. If the current suppression strategies are sustained, then 38.7 million lives globally will be saved this year, the epidemiologists at the Imperial College calculate.
But epidemiologists aren’t economists. We can not stay home for the rest of the year – the economic impact would be too high. We are three weeks into the shutdown and already factories are ceasing production, brick-and-mortar retail stores and restaurants are closed, unemployment spikes are unprecedented, commodity prices have plunged, and a wave of loan defaults is expected.
A colleague on a global pandemic response panel tells me the panel’s best estimate is that the US economy will rebound rapidly, but only if the nation returns to work in 60 days. After that, it’s anyone’s guess. No one, not even the experts, are willing to estimate the full economic impact of COVID-19. It will depend on how long it takes to get back to work and how many times we will be sent back home.”
https://mailchi.mp/lifespanbook.com/my-covid-19-update-2572786

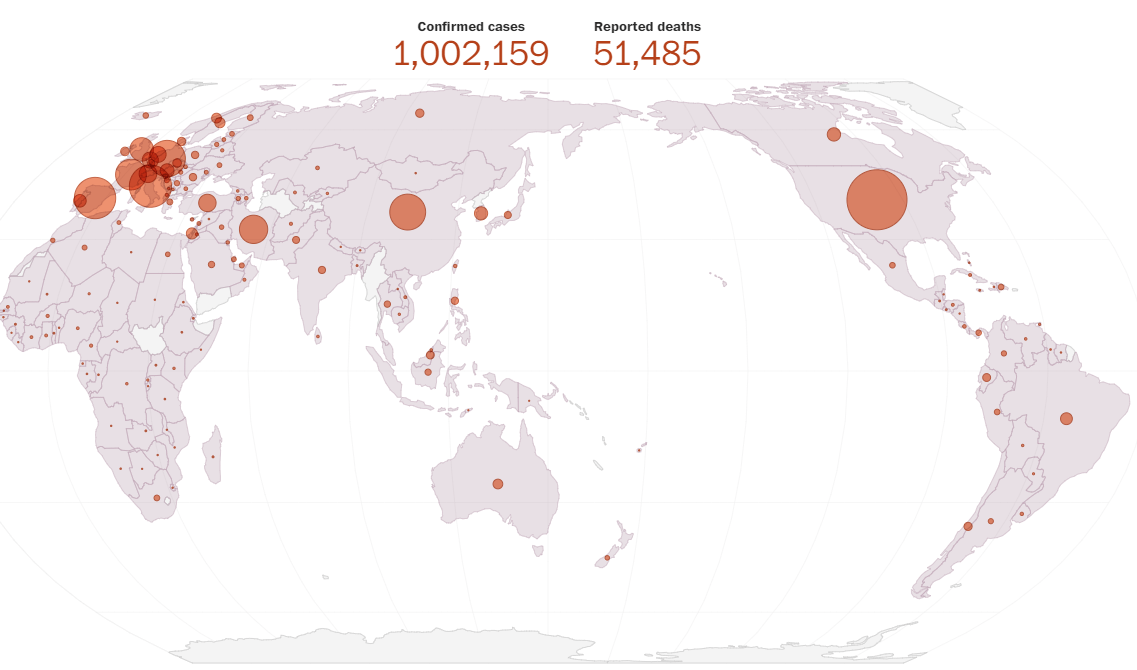
Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China | Nature Medicine
As of 29 February 2020 there were 79,394 confirmed cases and 2,838 deaths from COVID-19 in mainland China. Of these, 48,557 cases and 2,169 deaths occurred in the epicenter, Wuhan. A key public health priority during the emergence of a novel pathogen is estimating clinical severity, which requires properly adjusting for the case ascertainment rate and the delay between symptoms onset and death. Using public and published information, we estimate that the overall symptomatic case fatality risk (the probability of dying after developing symptoms) of COVID-19 in Wuhan was 1.4% (0.9–2.1%), which is substantially lower than both the corresponding crude or naïve confirmed case fatality risk (2,169/48,557 = 4.5%) and the approximator1 of deaths/deaths + recoveries (2,169/2,169 + 17,572 = 11%) as of 29 February 2020. Compared to those aged 30–59 years, those aged below 30 and above 59 years were 0.6 (0.3–1.1) and 5.1 (4.2–6.1) times more likely to die after developing symptoms. The risk of symptomatic infection increased with age (for example, at ~4% per year among adults aged 30–60 years).

Simple trick that will help your glycans to protect you from COVID-19 – YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SpRKz1YaDJM

Cyto-Immuno-Therapy for Cancer: A Pathway Elicited by Tumor-Targeted, Cytotoxic Drug-Packaged Bacterially Derived Nanocells – ScienceDirect
EnGenIC is a local Sydney company that I had the great pleasure of working with for some time.
They are a group of Aussie scientists showing the world that Australia is still a centre of innovation, especially in medial technology.
They’ve been working hard for this amazing cancer treatment technology and have recently just been published again. This latest publication is linked below.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1535610820300908

3.26.20 is Fantastic Fungi Day. Join the Global Mycelium Network!


Dietary Intakes of Minerals, Essential and Toxic Trace Elements for Adults from Eragrostis tef L.: A Nutritional Assessment
“This study analysed the contents of thirty-six mineral and trace elements in teff (Eragrostis tef L.) grains. What is more, dietary intakes were calculated. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to assess mineral and trace element contents. Consequently, the appropriate Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) or adequate intake (AI), and provisional tolerable weekly intake (PTWI) or provisional tolerable monthly intake (PTMI) values for adults were determined according to the Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) and Institute of Medicine (IOM) regulations. Teff is a significant contributor to RDAs and AIs for females in the following order: Mn > Cu > Zn ≥ Mg > Fe ≥ P and Ca. For males, teff contributes in the order, Mn > Cu > Fe > Zn ≥ P ≥ Mg > and Ca. The concentration of arsenic (65.9 µg/kg) in brown teff originating in Bolivia exceeded the average acceptable value set by Reg. No. 1881 of 6–50 µg/kg in cereals consumed in the EU. The PTWIs or PTMIs for Al, Cd, Sn and Hg were all under 7%, which is below the limits of toxic element intake related to the body weight of 65 kg for adult females and 80 kg for males, set by the FAO/WHO. Teff grains can be recommended as a valuable and safe source of minerals and trace elements.”
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Dietary Intakes of Minerals, Essential and Toxic Trace Elements for Adults from Eragrostis tef L.: A Nutritional Assessment | HTML


Matched Weight Loss Through Intermittent or Continuous Energy Restriction Does Not Lead To Compensatory Increases in Appetite and Eating Behavior
“Controlled ≥5% WL via CER or IER did not differentially affect changes in body composition, reductions in hunger, and improvements in eating behavior traits. This suggests that neither CER nor IER lead to compensatory adaptations in appetite in women with overweight/obesity. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT03447600.”
https://academic.oup.com/jn/article-abstract/150/3/623/5673202?redirectedFrom=fulltext

High-Quality Plant-Based Protein Blends Compared to Whey Protein—A Double-Blind Randomized, Cross-Over, Clinical Trial
A new study shows that plant based protein, selected for thier status as high quality, does not compare equally to animal based protein. The study found the plant based protein to be 40% less effective than the animal based Whey protein.

Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting | Annual Review of Nutrition
“Intermittent fasting regimens are hypothesized to influence metabolic regulation via effects on (a) circadian biology, (b) the gut microbiome, and (c) modifiable lifestyle behaviors, such as sleep. If proven to be efficacious, these eating regimens offer promising nonpharmacological approaches to improving health at the population level, with multiple public health benefits.”

The Neuroprotective Properties of Hericium erinaceus in Glutamate-Damaged Differentiated PC12 Cells and an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model
“Hericium erinaceus, an edible and medicinal mushroom, displays various pharmacological activities in the prevention of dementia in conditions such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. The present study explored the neuroprotective effects of H. erinaceus mycelium polysaccharide-enriched aqueous extract (HE) on an l-glutamic acid (l-Glu)-induced differentiated PC12 (DPC12) cellular apoptosis model and an AlCl3 combined with d-galactose-induced Alzheimer’s disease mouse model.”

Hypothesis of mtor and AMPK in infants and children
According to a study conducted in the 1980’s, babies have between 2 and 28 days of no growth, then a day of strong growth.
Maybe mtor suppression is useful even in young children and is suppressed during those 2 to 28 days at which point the body switches to anabolic and AMPK suppression.
Maybe children and adults aren’t so different in regards to the importance of cycling between expression and suppression of mtor and AMPK.
We will need to confirm that study and it’s data. We would also need a study that could track mtor and AMPK in babies as they go, daily or perhaps every 2 days as the smaple interval.

Babies – a fantastic series on babies and nutrition
“Babies” talks about the process and development of human babies. It follows new families for 1 year with close observation and correlates parenting bahaviours and tactics, human society aspects, nutrition, Microbiome and much more.
I’d recommended this to anyone wishing to understand nutrition in general but, especially of course, for babies.
Check it out at the below link
https://www.netflix.com/title/80117833?s=a&trkid=13747225&t=more

Finding good food
I visited my local https://thesourcebulkfoods.com.au/ store at Rhodes the other day and found some great products. Among them was Kakadu plum powder and grass fed bone broth powder. The owner of the store and staff were very nice and very helpful. If you are looking for ingredients for your healthy meals then this is one good place to start. They have stores all around Australia and in some other regions as well and each seems to be owned by individuals or families under a franchise model. Each franchise also seems to have a fair bit of flexibility around sourcing ingredients so don’t be afraid to ask for something if it’s not already in store.
I will keep you up to date on new findings, please let us know if you find any places to get great quality ingredients.

Relationships Between REM And NREM In The NREM-REM Sleep Cycle: A Review On Competing Concepts – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• This is a broad perspective, historical review of the relationships between REM and NREM sleep.
• Deep insights into of the most relevant and competing concepts.
• Features a new “asymmetrical†hypothesis on the distal end of ultradian cycles.
• REM sleep potentially viewed as an evolutionary remnant of ectotherms sleep.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389945720300757

An overlooked danger of ketogenic diets Making the case that ketone bodies induce vascular damage by the same mechanisms as glucose – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• Low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diets are associated with increased mortality
• Ketone bodies form adducts with proteins by the same mechanisms as glucose
• Ketone bodies and glucose may lead to vascular injury through common pathways
• Dietary ketosis as a means of avoiding glucose-induced vascular damage is futile
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900720300460
Editors note: We have recently posted about the dangers of following fads and trends without full consideration. These eating strategies are meant for specific outcomes for specific people and for specific time windows.
Please ensure you do some research before you embark on any of these trending eating strategies.

Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases
“In recent years, natural products, which originate from plants, animals, and fungi, together with their bioactive compounds have been intensively explored and studied for their therapeutic potentials for various diseases such as cardiovascular, diabetes, hypertension, reproductive, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are characterized by the progressive dysfunction and loss of neuronal structure and function that resulted in the neuronal cell death. Since the multifactorial pathological mechanisms are associated with neurodegeneration, targeting multiple mechanisms of actions and neuroprotection approach, which involves preventing cell death and restoring the function to damaged neurons, could be promising strategies for the prevention and therapeutic of neurodegenerative diseases. Natural products have emerged as potential neuroprotective agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. This review focused on the therapeutic potential of natural products and their bioactive compounds to exert a neuroprotective effect on the pathologies of neurodegenerative diseases.”

Inhibition of USP7 activity selectively eliminates senescent cells in part via restoration of p53 activity – He – – Aging Cell – Wiley Online Library
“The accumulation of senescent cells (SnCs) is a causal factor of various ageâ€related diseases as well as some of the side effects of chemotherapy. Pharmacological elimination of SnCs (senolysis) has the potential to be developed into novel therapeutic strategies to treat these diseases and pathological conditions. Here we show that ubiquitinâ€specific peptidase 7 (USP7) is a novel target for senolysis because inhibition of USP7 with an inhibitor or genetic depletion of USP7 by RNA interference induces apoptosis selectively in SnCs. The senolytic activity of USP7 inhibitors is likely attributable in part to the promotion of the human homolog of mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) ubiquitination and degradation by the ubiquitin–proteasome system. This degradation increases the levels of p53, which in turn induces the proâ€apoptotic proteins PUMA, NOXA, and FAS and inhibits the interaction of BCLâ€XL and BAK to selectively induce apoptosis in SnCs. Further, we show that treatment with a USP7 inhibitor can effectively eliminate SnCs and suppress the senescenceâ€associated secretory phenotype (SASP) induced by doxorubicin in mice. These findings suggest that small molecule USP7 inhibitors are novel senolytics that can be exploited to reduce chemotherapyâ€induced toxicities and treat ageâ€related diseases.”