Category: The ScienceScience and medical journal publications or articles and videos of reputable people using cited sources.
We search and collate these for you into a more digestible form in simply described categories.
If you wish to read more simplified or interpreted information, check our articles out in the Resources menu.
Science and medical journal publications or articles and videos of reputable people using cited sources.
We search and collate these for you into a more digestible form in simply described categories.
If you wish to read more simplified or interpreted information, check our articles out in the Resources menu.


Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research study finds honeybee venom rapidly kills aggressive breast cancer cells – ABC News
”
Venom from honeybees has been found to rapidly kill aggressive and hard-to-treat breast cancer cells, according to potentially groundbreaking new Australian research.
Key points:
- The research was published in the journal Nature Precision Oncology
- It found honeybee venom was effective in killing breast cancer cells
- Researchers say the discovery is exciting but there is a long way to go”

Massive Study of 24,000 Dreams Suggests They Really Are Continuations of Reality
“
“Research has repeatedly provided strong support for what sleep scientists refer to as the ‘continuity hypothesis of dreams‘: most dreams are a continuation of what is happening in everyday life,” researchers led by computer scientist Alessandro Fogli from Roma Tre University in Italy explain in a new study.
“It turns out that everyday life impacts dreaming (e.g. anxiety in life leads to dreams with negative affect) and vice versa (e.g. dreaming impacts problem-solving skills).”
These psychological theories date back to the work of Sigmund Freud and others in the 20th century, who spearheaded the notion that the hidden meanings of dreams could be unlocked when examined within the context of a person’s real-world experiences.”

Effects of oily fish intake on cognitive and socioemotional function in healthy 8–9-year-old children: the FiSK Junior randomized trial | The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | Oxford Academic
“Oily fish dose-dependently improved cognitive function, especially attention and cognitive flexibility, and reduced socioemotional problems. The results support the importance of n–3 LCPUFAs for optimal brain function and fish intake recommendations in children.”
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/112/1/74/5855515?searchresult=1

Effects of oily fish intake on cognitive and socioemotional function in healthy 8–9-year-old children: the FiSK Junior randomized trial | The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | Oxford Academic
“Oily fish dose-dependently improved cognitive function, especially attention and cognitive flexibility, and reduced socioemotional problems. The results support the importance of n–3 LCPUFAs for optimal brain function and fish intake recommendations in children.”
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/112/1/74/5855515?searchresult=1
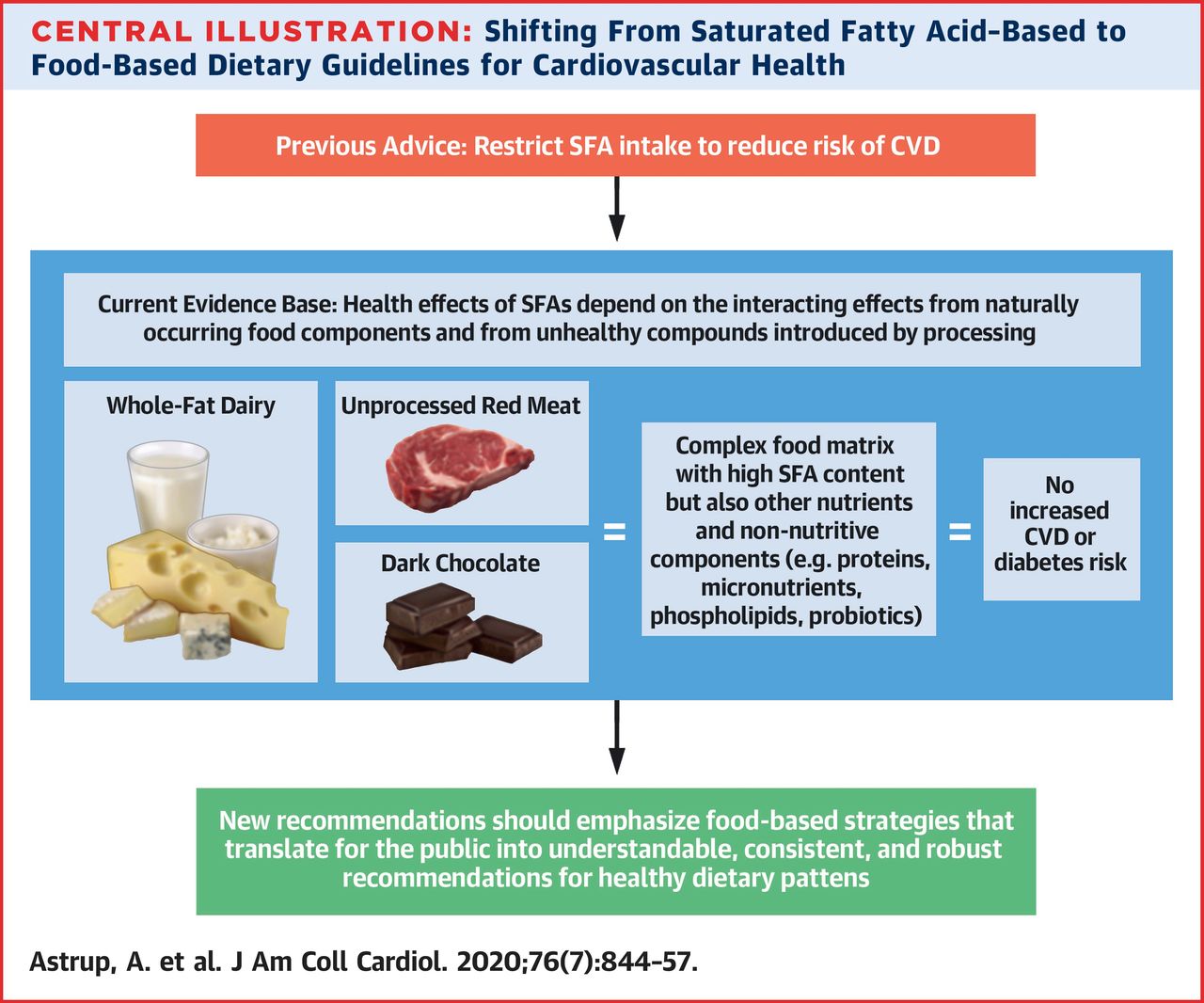
Saturated Fats and Health: AÂ Reassessment and Proposal for Food-Based Recommendations | JACC: Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Dave Asprey seems to do a good job at explaining what this study means:
“Something truly epic happened today that is going to change what you eat for years to come. Truly epic. The Journal of the American College of cardiology published a groundbreaking paper today admitting something that you already knew if you had been on the Bulletproof Diet for the last 10 years. (Yes, I am feeling slightly vindicated after receiving so much resistance after writing The Bulletproof Diet, which eventually helped people lose about 1,000,000 pounds!)This new paper, which uses data from studying 135,000 people overtime, finds:-Saturated fat from meat and dairy do not cause an increase in cardiovascular disease, and reduce stroke risk.-Polyunsaturated fats increase risk of cardiovascular disease.-Different fats do different things-Cutting saturated fat does not reduce death rate-the 25% of people eating the highest saturated fat intake (about ∼14% of calories) had lower risk of stroke-Only 5% of fat should be polyunsaturated for lowest death. This is effectively a deathblow to vegan and plant-based practices, which make people sick over time because they contain almost all polyunsaturated fats. It’s one reason I got sicker when I was a vegan. (It takes 2 years to replace half your cell membrane fats when you change your diet.)”

Scientists inspired by ‘Star Wars’ create artificial skin able to feel – Reuters
SINGAPORE (Reuters) – Singapore researchers have developed “electronic skin†capable of recreating a sense of touch, an innovation they hope will allow people with prosthetic limbs to detect objects, as well as feel texture, or even temperature and pain.
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-singapore-skin-idUSKBN24Z13D

Scientists inspired by ‘Star Wars’ create artificial skin able to feel – Reuters
SINGAPORE (Reuters) – Singapore researchers have developed “electronic skin†capable of recreating a sense of touch, an innovation they hope will allow people with prosthetic limbs to detect objects, as well as feel texture, or even temperature and pain.
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-singapore-skin-idUSKBN24Z13D

Niacin Increases NAD+ Significantly in Human Trial | Lifespan.io
The results of a new human trial using niacin shed new light on its role in NAD+ biology [1].
The trial participants were given a steadily increasing dose of niacin, starting at 250 mg/day to 750-1000 mg/day over a 4-month period, then a 10-month follow-up treatment period. The participants were organized into a study group of individuals with mitochondrial myopathy and a control group of healthy age-matched people consisting of two healthy people for each patient with mitochondrial myopathy. All the study participants were placed on the same niacin supplementation regimen.
The researchers report that niacin treatment increased muscle NAD+ levels by 1.3-fold at 4 months and 2.3-fold after 10 months in the study group.
https://www.lifespan.io/news/niacin-increases-nad-significantly-in-human-trial/

Niacin Increases NAD+ Significantly in Human Trial | Lifespan.io
The results of a new human trial using niacin shed new light on its role in NAD+ biology [1].
The trial participants were given a steadily increasing dose of niacin, starting at 250 mg/day to 750-1000 mg/day over a 4-month period, then a 10-month follow-up treatment period. The participants were organized into a study group of individuals with mitochondrial myopathy and a control group of healthy age-matched people consisting of two healthy people for each patient with mitochondrial myopathy. All the study participants were placed on the same niacin supplementation regimen.
The researchers report that niacin treatment increased muscle NAD+ levels by 1.3-fold at 4 months and 2.3-fold after 10 months in the study group.
https://www.lifespan.io/news/niacin-increases-nad-significantly-in-human-trial/

Niacin Increases NAD+ Significantly in Human Trial | Lifespan.io
The results of a new human trial using niacin shed new light on its role in NAD+ biology [1].
The trial participants were given a steadily increasing dose of niacin, starting at 250 mg/day to 750-1000 mg/day over a 4-month period, then a 10-month follow-up treatment period. The participants were organized into a study group of individuals with mitochondrial myopathy and a control group of healthy age-matched people consisting of two healthy people for each patient with mitochondrial myopathy. All the study participants were placed on the same niacin supplementation regimen.
The researchers report that niacin treatment increased muscle NAD+ levels by 1.3-fold at 4 months and 2.3-fold after 10 months in the study group.
https://www.lifespan.io/news/niacin-increases-nad-significantly-in-human-trial/

Diluting blood plasma rejuvenates tissue and reverses aging – Neuroscience News
Summary: Diluting the blood plasma of older mice has a stronger rejuvenating effect on the brain, liver, and muscles than transplanting the blood of younger mice.
Source: UC Berkeley
In 2005, University of California, Berkeley, researchers made the surprising discovery that making conjoined twins out of young and old mice — such that they share blood and organs — can rejuvenate tissues and reverse the signs of aging in the old mice. The finding sparked a flurry of research into whether a youngster’s blood might contain special proteins or molecules that could serve as a “fountain of youth†for mice and humans alike.
But a new study by the same team shows that similar age-reversing effects can be achieved by simply diluting the blood plasma of old mice — no young blood needed.

Cyto-Immuno-Therapy for Cancer: A Pathway Elicited by Tumor-Targeted, Cytotoxic Drug-Packaged Bacterially Derived Nanocells – ScienceDirect
EnGenIC is a local Sydney company that I had the great pleasure of working with for some time.
They are a group of Aussie scientists showing the world that Australia is still a centre of innovation, especially in medial technology.
They’ve been working hard for this amazing cancer treatment technology and have recently just been published again. This latest publication is linked below.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1535610820300908

Dietary Intakes of Minerals, Essential and Toxic Trace Elements for Adults from Eragrostis tef L.: A Nutritional Assessment
“This study analysed the contents of thirty-six mineral and trace elements in teff (Eragrostis tef L.) grains. What is more, dietary intakes were calculated. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to assess mineral and trace element contents. Consequently, the appropriate Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) or adequate intake (AI), and provisional tolerable weekly intake (PTWI) or provisional tolerable monthly intake (PTMI) values for adults were determined according to the Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) and Institute of Medicine (IOM) regulations. Teff is a significant contributor to RDAs and AIs for females in the following order: Mn > Cu > Zn ≥ Mg > Fe ≥ P and Ca. For males, teff contributes in the order, Mn > Cu > Fe > Zn ≥ P ≥ Mg > and Ca. The concentration of arsenic (65.9 µg/kg) in brown teff originating in Bolivia exceeded the average acceptable value set by Reg. No. 1881 of 6–50 µg/kg in cereals consumed in the EU. The PTWIs or PTMIs for Al, Cd, Sn and Hg were all under 7%, which is below the limits of toxic element intake related to the body weight of 65 kg for adult females and 80 kg for males, set by the FAO/WHO. Teff grains can be recommended as a valuable and safe source of minerals and trace elements.”
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Dietary Intakes of Minerals, Essential and Toxic Trace Elements for Adults from Eragrostis tef L.: A Nutritional Assessment | HTML


Matched Weight Loss Through Intermittent or Continuous Energy Restriction Does Not Lead To Compensatory Increases in Appetite and Eating Behavior
“Controlled ≥5% WL via CER or IER did not differentially affect changes in body composition, reductions in hunger, and improvements in eating behavior traits. This suggests that neither CER nor IER lead to compensatory adaptations in appetite in women with overweight/obesity. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT03447600.”
https://academic.oup.com/jn/article-abstract/150/3/623/5673202?redirectedFrom=fulltext

High-Quality Plant-Based Protein Blends Compared to Whey Protein—A Double-Blind Randomized, Cross-Over, Clinical Trial
A new study shows that plant based protein, selected for thier status as high quality, does not compare equally to animal based protein. The study found the plant based protein to be 40% less effective than the animal based Whey protein.

Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting | Annual Review of Nutrition
“Intermittent fasting regimens are hypothesized to influence metabolic regulation via effects on (a) circadian biology, (b) the gut microbiome, and (c) modifiable lifestyle behaviors, such as sleep. If proven to be efficacious, these eating regimens offer promising nonpharmacological approaches to improving health at the population level, with multiple public health benefits.”

The Neuroprotective Properties of Hericium erinaceus in Glutamate-Damaged Differentiated PC12 Cells and an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model
“Hericium erinaceus, an edible and medicinal mushroom, displays various pharmacological activities in the prevention of dementia in conditions such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. The present study explored the neuroprotective effects of H. erinaceus mycelium polysaccharide-enriched aqueous extract (HE) on an l-glutamic acid (l-Glu)-induced differentiated PC12 (DPC12) cellular apoptosis model and an AlCl3 combined with d-galactose-induced Alzheimer’s disease mouse model.”

Hypothesis of mtor and AMPK in infants and children
According to a study conducted in the 1980’s, babies have between 2 and 28 days of no growth, then a day of strong growth.
Maybe mtor suppression is useful even in young children and is suppressed during those 2 to 28 days at which point the body switches to anabolic and AMPK suppression.
Maybe children and adults aren’t so different in regards to the importance of cycling between expression and suppression of mtor and AMPK.
We will need to confirm that study and it’s data. We would also need a study that could track mtor and AMPK in babies as they go, daily or perhaps every 2 days as the smaple interval.

Babies – a fantastic series on babies and nutrition
“Babies” talks about the process and development of human babies. It follows new families for 1 year with close observation and correlates parenting bahaviours and tactics, human society aspects, nutrition, Microbiome and much more.
I’d recommended this to anyone wishing to understand nutrition in general but, especially of course, for babies.
Check it out at the below link
https://www.netflix.com/title/80117833?s=a&trkid=13747225&t=more

Relationships Between REM And NREM In The NREM-REM Sleep Cycle: A Review On Competing Concepts – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• This is a broad perspective, historical review of the relationships between REM and NREM sleep.
• Deep insights into of the most relevant and competing concepts.
• Features a new “asymmetrical†hypothesis on the distal end of ultradian cycles.
• REM sleep potentially viewed as an evolutionary remnant of ectotherms sleep.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389945720300757

An overlooked danger of ketogenic diets Making the case that ketone bodies induce vascular damage by the same mechanisms as glucose – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• Low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diets are associated with increased mortality
• Ketone bodies form adducts with proteins by the same mechanisms as glucose
• Ketone bodies and glucose may lead to vascular injury through common pathways
• Dietary ketosis as a means of avoiding glucose-induced vascular damage is futile
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900720300460
Editors note: We have recently posted about the dangers of following fads and trends without full consideration. These eating strategies are meant for specific outcomes for specific people and for specific time windows.
Please ensure you do some research before you embark on any of these trending eating strategies.

Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases
“In recent years, natural products, which originate from plants, animals, and fungi, together with their bioactive compounds have been intensively explored and studied for their therapeutic potentials for various diseases such as cardiovascular, diabetes, hypertension, reproductive, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are characterized by the progressive dysfunction and loss of neuronal structure and function that resulted in the neuronal cell death. Since the multifactorial pathological mechanisms are associated with neurodegeneration, targeting multiple mechanisms of actions and neuroprotection approach, which involves preventing cell death and restoring the function to damaged neurons, could be promising strategies for the prevention and therapeutic of neurodegenerative diseases. Natural products have emerged as potential neuroprotective agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. This review focused on the therapeutic potential of natural products and their bioactive compounds to exert a neuroprotective effect on the pathologies of neurodegenerative diseases.”

Inhibition of USP7 activity selectively eliminates senescent cells in part via restoration of p53 activity – He – – Aging Cell – Wiley Online Library
“The accumulation of senescent cells (SnCs) is a causal factor of various ageâ€related diseases as well as some of the side effects of chemotherapy. Pharmacological elimination of SnCs (senolysis) has the potential to be developed into novel therapeutic strategies to treat these diseases and pathological conditions. Here we show that ubiquitinâ€specific peptidase 7 (USP7) is a novel target for senolysis because inhibition of USP7 with an inhibitor or genetic depletion of USP7 by RNA interference induces apoptosis selectively in SnCs. The senolytic activity of USP7 inhibitors is likely attributable in part to the promotion of the human homolog of mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) ubiquitination and degradation by the ubiquitin–proteasome system. This degradation increases the levels of p53, which in turn induces the proâ€apoptotic proteins PUMA, NOXA, and FAS and inhibits the interaction of BCLâ€XL and BAK to selectively induce apoptosis in SnCs. Further, we show that treatment with a USP7 inhibitor can effectively eliminate SnCs and suppress the senescenceâ€associated secretory phenotype (SASP) induced by doxorubicin in mice. These findings suggest that small molecule USP7 inhibitors are novel senolytics that can be exploited to reduce chemotherapyâ€induced toxicities and treat ageâ€related diseases.”

The effects of resveratrol on lipid profiles and liver enzymes
“This meta-analysis demonstrated that resveratrol supplementation among patients with MetS and related disorders significantly reduced total cholesterol and increased GGT concentrations, but did not affect triglycerides, LDL-, HDL-cholesterol, ALT, and AST concentrations. This data suggests that resveratrol may have a potential cardio-protective effect in patients with MetS and related disorders”

Reproductive Aging Process Reversed in Mice | Technology Networks
Dr. David Sinclair posted this morning on reversing the effects of aging on reproductive viability.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/sinclairda_our-research-teams-just-published-a-promising-activity-6633781677380423680-fXys

Geroncogenesis: Metabolic Changes during Aging as a Driver of Tumorigenesis: Cancer Cell
“Why does cancer risk increase as we age? Frequently attributed to the multi-hit hypothesis and the time required to accumulate genomic mutations, this question is a matter of ongoing debate. Here, we propose that the normal decline in oxidative metabolism during aging constitutes an early and important “hit†that drives tumorigenesis. Central to these metabolic changes are the sirtuins, a family of NAD+-dependent deacylases that have evolved as coordinators of physiological responses to nutrient intake and energetic demand. Thus, the modulation of sirtuins might be a fruitful approach to reversing the age-related metabolic changes that could underlie tumorigenesis.”
https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(13)00534-5

Atg11 is required for initiation of glucose starvation-induced autophagy
“How energy deprivation induces macroautophagy/autophagy is not fully understood. Here, we show that Atg11, a receptor protein for cargo recognition in selective autophagy, is required for the initiation of glucose starvation-induced autophagy.”

Mitophagy and DNA damage signaling in human aging
Highlights
•DNA damage regulates mitophagy induction and mitochondrial homeostasis.
•Nuclear-mitochondrial signaling modulates aging and age-associated disorders.
•Combinatorial approaches targeting DNA repair and mitophagy could promote healthy aging.
Mitophagy and DNA damage signaling in human aging – ScienceDirect

Education and age-related decline in cognitive performance
Highlights
•Association of education and change in cognitive performance is negligible.
•Articles included in meta-analysis displayed high unexplained heterogeneity.
•Theories of cognitive aging need to be updated with regards to this association.
Education and age-related decline in cognitive performance: Systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies – ScienceDirect

Recent studies on anti-aging compounds with Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model organism – ScienceDirect
Extension of lifespan and amelioration of aging-associated phenotypes have been targets of many studies. Some of the established methods of increasing lifespan including dietary restriction and genetic manipulation are difficult to apply to humans, and their side effects are hard to predict. For that reason, it is important to discover compounds that can mimic the anti-aging actions or induce lifespan extension through different metabolisms within the cell. Here we summarize the recent studies to test various types of compounds and materials using budding yeast that show potential anti-aging effects.
Recent studies on anti-aging compounds with Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model organism – ScienceDirect

SIRT6 Finding the gas pedal on a slow sirtuin
“The class III histone deacetylase sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) modulates numerous functions in the cell by deacetylating histone lysine residues. Interestingly, SIRT6’s efficiency in in vitro experiments is far greater against substrates carrying long-chain fatty acyl modifications such as myristoylated lysine compared with acetylated counterparts, but the deacetylase activity can be stimulated by fatty acids and small-molecule allosteric modulators. A new study helps to explain this puzzling activation using a novel activator, thorough kinetic investigation, and mutagenesis studies. These data help elucidate the molecular requirements for activation of SIRT6 and provide a foundation for development of activators for therapeutic purposes.”

Banana Lectin Offers Hope Against Deadly Flu
“In a new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers have shown that an engineered compound based on a banana lectin, a protein called H84T, has real potential for clinical use against influenza.”

Improvement of cognitive function… preview & related info | Mendeley
“MMSE alone showed that oral intake of H. erinaceus significantly improved cognitive functions and prevented from the deterioration.”
https://www.mendeley.com/catalogue/improvement-cognitive-functions-oral-intake-hericium-erinaceus/

Mitochondria Found Independently Living in Blood | | LEAF
“The research team has published a new study, which shows that aside from the usual mitochondrial populations living inside our cells, there are also wandering mitochondria floating around in our bloodstreams. From time to time, mitochondria are found outside the cells, but only in the context of debris within platelets, so what are these intrepid mitochondria doing out there alone in the bloodstream?”
https://www.leafscience.org/mitochondria-found-independently-living-in-blood/

The Role of Cannabidiol (CBD) in Chronic Pain Management: An Assessment of Current Evidence | SpringerLink
“Given the growing challenges in chronic pain management coupled with the ongoing consequences of the opioid epidemic, pain management practitioners are looking into more effective, innovative, and safer alternatives to treat pain. Cannabis-based medicine had been described for hundreds of years but only recently have we seen the more scientific, evidence-based approach to its use, and ongoing investigations continue to explore its potential medical benefits. While historically more attention has been paid to the psychoactive component of the cannabis plant Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), there have been fewer scientific studies on the medical use of the cannabidiol (CBD) – a non-psychoactive component of the cannabis plant.”

Antimicrobial properties of Fomitopsis officinalis (Agarikon Mushroom) in the light of its bioactive metabolites: a review: Mycology: Vol 10, No 1
“According to several reports there is evidence of a broad-spectrum antibacterial and antiviral activity by F. officinalis, including pathogens like Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as Ortopox virus.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/21501203.2018.1536680

Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China – ScienceDirect
“By Jan 2, 2020, 41 admitted hospital patients had been identified as having laboratory-confirmed 2019-nCoV infection. Most of the infected patients were men (30 [73%] of 41); less than half had underlying diseases (13 [32%]), including diabetes (eight [20%]), hypertension (six [15%]), and cardiovascular disease (six [15%]). Median age was 49·0 years (IQR 41·0–58·0). 27 (66%) of 41 patients had been exposed to Huanan seafood market. One family cluster was found. Common symptoms at onset of illness were fever (40 [98%] of 41 patients), cough (31 [76%]), and myalgia or fatigue (18 [44%]); less common symptoms were sputum production (11 [28%] of 39), headache (three [8%] of 38), haemoptysis (two [5%] of 39), and diarrhoea (one [3%] of 38). Dyspnoea developed in 22 (55%) of 40 patients (median time from illness onset to dyspnoea 8·0 days [IQR 5·0–13·0]). 26 (63%) of 41 patients had lymphopenia. All 41 patients had pneumonia with abnormal findings on chest CT. Complications included acute respiratory distress syndrome (12 [29%]), RNAaemia (six [15%]), acute cardiac injury (five [12%]) and secondary infection (four [10%]). 13 (32%) patients were admitted to an ICU and six (15%) died. Compared with non-ICU patients, ICU patients had higher plasma levels of IL2, IL7, IL10, GSCF, IP10, MCP1, MIP1A, and TNFα.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673620301835

Fasting Activates Fatty Acid Oxidation to Enhance Intestinal Stem Cell Function during Homeostasis and Aging: Cell Stem Cell
Highlights
• Fasting induces fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in intestinal stem and progenitor cells
• Aging reduces ISC numbers and function, correlating with decreased FAO
• PPAR/CPT1a-mediated FAO augments ISC function in aging and during regeneration
• PPARδ agonists boost and restore ISC and progenitor function in young and old age
https://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/fulltext/S1934-5909(18)30163-2

Kynurenine pathway, NAD+ synthesis, and mitochondrial function: Targeting tryptophan metabolism to promote longevity and healthspan – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• The kynurenine pathway has recently been identified as a promising target to increase healthy longevity.
• Targeted inhibition of kynurenine pathway activity may alleviate several pathological conditions and promote healthspan.
• Changes to the production and recycling of NAD+ is a likely mediator of the beneficial effects of kynurenine pathway interventions.
• Mitochondrial function and dynamics represent NAD+-dependent processes downstream of kynurenine metabolism that may mediate benefits during aging.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S053155651930765X

Aging and Caloric Restriction Modulate the DNA Methylation Profile of the Ribosomal RNA Locus in Human and Rat Liver
“We confirm previous findings, showing age-related hypermethylation, and describe, for the first time, that this gain in methylation also occurs in human hepatocytes. Furthermore, we show that age-related hypermethylation is enhanced in livers of rat upon CR at two and 10 months, and that at two months a trend towards the reduction of rRNA expression occurs. Collectively, our results suggest that CR modulates age-related regulation of methylation at the rDNA locus, thus providing an epigenetic readout of the pro-longevity effects of CR.”

Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team with new players
We talk about antioxidants a lot. Much of our longevity supplements are in fact antioxidants but, what are antioxidants and what is oxidisation and, furthermore, why do we care about it?

Oncotarget | From rapalogs to anti-aging formula
“Inhibitors of mTOR, including clinically available rapalogs such as rapamycin (Sirolimus) and Everolimus, are gerosuppressants, which suppress cellular senescence. Rapamycin slows aging and extends life span in a variety of species from worm to mammals. Rapalogs can prevent age-related diseases, including cancer, atherosclerosis, obesity, neurodegeneration and retinopathy and potentially rejuvenate stem cells, immunity and metabolism. Here, I further suggest how rapamycin can be combined with metformin, inhibitors of angiotensin II signaling (Losartan, Lisinopril), statins (simvastatin, atorvastatin), propranolol, aspirin and a PDE5 inhibitor. Rational combinations of these drugs with physical exercise and an anti-aging diet (Koschei formula) can maximize their anti-aging effects and decrease side effects.”

Deuterium-Depleted Water, Water Filtration, Alkaline Water, & Much More!
Water, simple H2O right? Not quite. In this podcast, Ben Greenfield speaks with Robert Slovak about different types of water and possible benefits.

Metformin mediates cardioprotection against agingâ€induced ischemic necroptosis – Li – – Aging Cell – Wiley Online Library
“Notably, metformin treatment disrupted p62â€RIP1â€RIP3 complexes and effectively repressed I/Râ€induced necroptosis in aged hearts, ultimately reducing mortality in this model. These findings highlight previously unknown mechanisms of agingâ€related myocardial ischemic vulnerability: p62â€necrosomeâ€dependent necroptosis. Metformin acts as a cardioprotective agent that inhibits this unfavorable chain mechanism of agingâ€related I/R susceptibility.”

Resveralogues: From Novel Ageing Mechanisms to New Therapies? – Abstract – Gerontology – Karger Publishers
“For much of the 20th century the ageing process was thought to be the result of the interplay of many different biological processes, each with relatively small effects on organismal lifespan. However, this model is no longer tenable. Rather it seems a few biological mechanisms, including nutrient sensing, telomere attrition and cellular senescence, mediate large effects on health and longevity. Biogerontology may have suffered from initial delusions of complexity. However, we argue that it is premature to assume either that the list of biological processes influencing lifespan is now comprehensive or that these mechanisms act independently of each other.”

IJMS | Free Full-Text | BCL-xL, a Mitochondrial Protein Involved in Successful Aging: From C. elegans to Human Centenarians
“B-Cell Lymphoma-extra-large (BCL-xL) is involved in longevity and successful aging, which indicates a role for BCL-xL in cell survival pathway regulation. Beyond its well described role as an inhibitor of apoptosis by preventing cytochrome c release, BCL-xL has also been related, indirectly, to autophagy and senescence pathways.”

NAD+ therapy in age-related degenerative disorders: A benefit/risk analysis – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• NAD+ plays an important protective role in some age-related degenerative disease states.
• NAD+ can improve mitochondrial function and maintain sufficient levels of ATP.
• NAD+ can influences DNA repair, and immune and longevity processes.
• Raising NAD+ levels can balance energy needs with supply and protect against oxidative damage and inflammation.
• Further clinical trials are necessary to validate NAD+ therapy in ageing and disease.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0531556519307582

Cordyceps militaris induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through TNF-α/TNFR1-mediated inhibition of NF-κB phosphorylation | BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies | Full Text
“These results suggest that C. militaris inhibited ovarian cancer cell proliferation, survival, and migration, possibly through the coordination between TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling and NF-κB activation. Taken together, our findings provide a new insight into a novel treatment strategy for ovarian cancer using C. militaris.”
https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12906-019-2780-5

The Healthy Grain BARLEYmaxâ„¢ and Kebari Barley
Developed by CSIRO scientists, BARLEYmaxTM wholegrains represent the next evolution of superfoods, an enhanced wholegrain. The credentials of BARLEYmaxTM begin with it’s history. It was bred using traditional plant breeding processes, and is 100% GM free. The enhanced wholegrain discovered by Dr Morell and his team at the CSIRO contains two times the dietary fibre and four times the resistant starch of a regular grain.
The Healthy Grain BARLEYmaxâ„¢ and Kebari Barley

Zinc transporters maintain longevity by influencing insulin/IGFâ€1 activity in Caenorhabditis elegans – Novakovic – – FEBS Letters – Wiley Online Library
“Adequate dietary intake of essential metals such as zinc is important for maintaining homeostasis. Abnormal zinc intake in Caenorhabditis elegans has been shown to increase or decrease normal lifespan by influencing the insulin/IGFâ€1 pathway. Distribution of zinc is achieved by a family of highly conserved zinc transport proteins (ZIPT in C. elegans). This study investigated the role of the zipt family of genes and show that depletion of individual zipt genes results in a decreased lifespan”
https://febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/1873-3468.13725

The somatic mutation landscape of the human body | Genome Biology | Full Text
“Somatic mutations in healthy tissues contribute to aging, neurodegeneration, and cancer initiation, yet they remain largely uncharacterized.”
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-019-1919-5

Study finds losing a night of sleep may increase blood levels of Alzheimer’s biomarker | EurekAlert! Science News
“A preliminary study by researchers at Uppsala University has found that when young, healthy men were deprived of just one night of sleep, they had higher levels of tau – a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease – in their blood than when they had a full, uninterrupted night of rest. The study is published in the medical journal Neurology.”
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2020-01/uu-sfl010820.php

Biologists identify pathways that extend lifespan by 500%
“Because alteration of the IIS pathways yields a 100 percent increase in lifespan and alteration of the TOR pathway yields a 30 percent increase, the double mutant would be expected to live 130 percent longer. But instead, its lifespan was amplified by 500 percent.
“Despite the discovery in C. elegans of cellular pathways that govern aging, it hasn’t been clear how these pathways interact,” said Hermann Haller, M.D., president of the MDI Biological Laboratory. “By helping to characterize these interactions, our scientists are paving the way for much-needed therapies to increase healthy lifespan for a rapidly aging population.””
https://phys.org/news/2020-01-biological-scientists-pathways-lifespan.html

Fad or Future Podcast | Hosted by Joey Thurman
“I’ve been talking about the benefits of “stressed plants” a lot of late. And that’s because of xenohormesis. I believe that when we eat plants that have been stressed, our bodies pick up on those chemical cues and allows us to get the stress benefits. That is, our own hormesis benefits. This is one of the reasons why I believe organic foods are better for us. More here from my discussion with Joey Thurman”
David A Sinclair
Full link here:

3 Ways We May Be Able To Reverse Aging, From A Microbiologist
“Organic foods aren’t held with gloves. They’re a little bit more stressed out. The more stressed out your food is the brighter colors they’ll have because they’re producing these colors as a defense,” Sinclair explains.
Those bright colors, he adds, are indicators that the food has produced “xenohormesis molecules,” which activate our sirtuins that give our bodies an extra boost for longevity.
https://www.mindbodygreen.com/articles/3-easy-hacks-for-longevity-from-an-aging-microbiologist

Bulletproof 30-Day Sleep Challenge
Sleep better in the new year with the Bulletproof 30-Day Sleep Challenge. For the duration of the challenge, you’ll employ science-backed methods designed to help you sleep deeper, so you wake up refreshed.The Bulletproof 30-Day Sleep Challenge is laid out as a series of four steps. When implemented together, they’ll make you a champion at sleep, and as a result, a champion at life.  The Sleep Challenge will help you sleep better by focusing on sleep hygiene, stress, diet, and tracking your progress.The order you do them in doesn’t matter — as long as you see to all four components before starting, you’re golden.
Bulletproof 30-Day Sleep Challenge

Fisetin | | LEAF
“Fisetin, like many plant polyphenols, is known to have antioxidant properties and demonstrates the specific biological activity of protecting functional macromolecules against stress, resulting in a benefit to cellular cytoprotection. It is also known to have anti-inflammatory, chemopreventive, and chemotherapeutic properties.
Finally, more recently, it has also shown promise as a senolytic, a compound that encourages aged or damaged senescent cells to destroy themselves rather than lingering in the body and contributing to the chronic, age-related inflammation known as “inflammagingâ€, which is associated with a wide range of age-related diseases.
Since fisetin has a good safety profile, Mayo Clinic followed these mouse studies by launching three trials to see if the compound is effective for humans.”
Human Clinical Trials with Fisetin:
- Nov 2018 to April 2020 Alleviation by Fisetin of Frailty, Inflammation, and Related Measures in Older Adults
- Feb 2018 to June 2020 Alleviation by Fisetin of Frailty, Inflammation, and Related Measures in Older Women
- Jan 2018 to April 2022 Inflammation and Stem Cells in Diabetic and Chronic Kidney Disease

Cannabidiol presents an inverted U-shaped dose-response curve in a simulated public speaking test. – PubMed – NCBI
“Compared to placebo, pretreatment with 300 mg of CBD significantly reduced anxiety during the speech. No significant differences in VAMS scores were observed between groups receiving CBD 150 mg, 600 mg and placebo.”

Exercise immunology: Future directions – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• The immune system is responsive to the physiological stress imposed by the exercise workload.
• Technological advances now allow a systems biology approach to exercise immunology.
• The immune response to exercise is influenced by small-molecule metabolites and proteins.
• Immunometabolism has provided new insights into how metabolites influence immune function.
• Exercise has a modulating effect on gut microbial populations.

https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095254619301528

Centenarians: An excellent example of resilience for successful ageing – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• Centenarians maintain intrinsic capacity longer than individuals who display ordinary aging.
• Resilience is a determinant of health, and centenarians maintain it longer.
• Centenarians have specific genetic features.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0047637419302040

l-Theanine attenuates liver aging by inhibiting advanced glycation end products in d-galactose-induced rats and reversing an imbalance of oxidative stress and inflammation – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• Tea-derived l-theanine inhibited AGE production in d-galactose-induced aging rats.
• l-Theanine increased FoxO1 expression and antioxidative enzymes in aged livers.
• l-Theanine could reduce oxygen free radicals and maintain the redox balance.
• l-Theanine supplementation could protect against age-related liver damage.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0531556519306643

Role of Highâ€Density Lipoproteins in Cholesterol Homeostasis and Glycemic Control | Journal of the American Heart Association
Emerging evidence (summarized in Table) indicates that HDL†and apoAâ€I–targeted therapies are a potential option for conserving residual βâ€cell function and improving insulin sensitivity in patients who are progressing toward, or have already developed, T1DM and T2DM. The recent failures of HDLâ€raising agents in cardiovascular clinical outcome trials highlight the need to develop novel and innovative HDLâ€targeted approaches to achieve these goals. Elucidating the mechanism(s) underlying the antidiabetic functions of HDLs and apoAâ€I will also provide opportunities to identify and develop new HDLâ€targeted therapies for diabetes mellitus. Achievement of these goals could be particularly advantageous for patients with T1DM for whom treatment options are currently limited to insulin replacement therapy, and for patients with T2DM that are refractory to currently available therapies.

Table 1.Role of HDL and apoAâ€I in Glycemic Control, Insulin Sensitivity and βâ€Cell Function
Topic Outcome Reference
Association of HDLâ€C and apoAâ€I levels with glycemic control
Subjects with T2DM Serum HDLâ€C, apoAâ€I, and HDLâ€C/apoAâ€I levels are inversely associated with insulin resistance by HOMAâ€IR 9
Subjects with impaired glucose tolerance ApoAâ€I level is an independent risk factor for glucose tolerance 10
HDL and apoAâ€I in glucose disposal/insulin sensitivity
Primary human skeletal muscle cells ApoAâ€I improves insulinâ€dependent and â€independent glucose uptake 27
C2C12 skeletal muscle cells ApoAâ€I increases glucose uptake by phosphorylation of AMPK 35
Highâ€fat–fed C57BL/6 mice ApoAâ€I improves insulin sensitivity by reducing systemic and hepatic inflammation 40
db/db mice Longâ€term HDL infusion improves glucose tolerance by activating GSKâ€3 and AMPK in skeletal muscle 37
Pregnant female Wistar rats ApoAâ€I infusions increase insulin sensitivity, reduces systemic inflammation and protects against pregnancyâ€induced insulin resistance 45
Subjects with T2DM A single rHDL infusion reduces plasma glucose levels by increasing insulin secretion and promoting glucose uptake in skeletal muscle 2
HDL and apoAâ€I in βâ€cell function
Min6 insulinoma cells HDLs isolated from normal human plasma, rHDLs, and apoAâ€I increase Ins1 and Ins2 gene transcription and GSIS 58
Insâ€1E insulinoma cells ApoAâ€I increases Pdx1 gene transcription and GSIS 57
βTC3 insulinoma cells Incubation with HDL protects βTC3 cells against LDLâ€induced apoptosis 70
C57BL/6 mice ApoAâ€I infusions increase insulin secretion and improve glucose tolerance 52
Highâ€fat–fed C57BL/6 mice Shortâ€term apoAâ€I treatment increases GSIS and improves glucose clearance independent of insulin secretion 53
Mice with conditional deletion of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in β cells ApoAâ€I infusions increase GSIS in islets isolated from mice with elevated islet cholesterol levels 54
Healthy subjects and Min6 cells CETP inhibition increases plasma HDLâ€C, apoAâ€I, and insulin levels in normal human subjects. Plasma from these subjects also increases GSIS in Min6 cells pretreated with oxidized LDLs 60
Isolated human islets HDL protects human islets against oxidized LDLâ€induced apoptosis 71
Isolated human and mouse islets HDL protects human and mouse islets from interleukinâ€1β– and glucoseâ€induced apoptosis 72
AMPK indicates adenosine monophosphateâ€activated protein kinase; apoAâ€I, apolipoprotein Aâ€I; CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein; GSIS, glucoseâ€stimulated insulin secretion; GSK, glycogen synthase kinaseâ€3; HDL, highâ€density lipoprotein; HDLâ€C, highâ€density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMAâ€IR, Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; LDL, lowâ€density lipoprotein; rHDL, reconstituted HDL.

CoQ 10 enhances PGC1α and increases expression of mitochondrial antioxidant proteins in chronically ischemic swine myocardium | SpringerLink
“Four weeks of dietary CoQ10 in HM pigs enhances active, nuclear-bound PGC1α and increases the expression of ETC proteins within mitochondria of HM tissue.”

Reward does not facilitate visual perceptual learning until sleep occurs | PNAS
“First, we demonstrated a significantly larger offline performance gain over a 12-h interval including sleep in a reward group than that in a no-reward group. However, the offline performance gains over the 12-h interval without sleep were not significantly different with or without reward during training, indicating a crucial interaction between reward and sleep in VPL.”

The Vagus Nerve is Key to Well-Being | Elemental
“The vagus nerve, also called the “10th cranial nerve,†is the longest, largest, and most complex of the cranial nerves, and in some ways it’s also the least understood. Experts have linked its activity to symptom changes in people with migraine headaches, inflammatory bowel disease, depression, epilepsy, arthritis, and many other common ailments. The more science learns about the vagus nerve, the more it seems like a better understanding of its function could unlock new doors to treating all manner of human suffering.”
https://elemental.medium.com/science-confirms-that-the-vagus-nerve-is-key-to-well-being-c23fab90e211

Intermittent fasting: live ‘fast,’ live longer? | EurekAlert! Science News

“Mattson says studies have shown that this switch improves blood sugar regulation, increases resistance to stress and suppresses inflammation. Because most Americans eat three meals plus snacks each day, they do not experience the switch, or the suggested benefits.
In the article, Mattson notes that four studies in both animals and people found intermittent fasting also decreased blood pressure, blood lipid levels and resting heart rates.”
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2019-12/jhm-ifl121819.php

Muscle wasting disease linked to defective mitochondrial energy and NAD+ biosynthesis pathways – Science Mission
“Moreover, results showed that sarcopenia was also associated with reduced levels of enzymes involved in the recycling of NAD+, which acts as a metabolic sensor in the cell and regulates energy production pathways.”

Overspill of fat shown to cause Type 2 Diabetes – Science Mission
Fatty liver? You’re possibly one step away from type 2 diabetes.
Keep an eye on your ALT levels. Ask your doc for a lipid profile blood test and check it today!

Oleic acid influences the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via DNA Methylation and may predispose to obesity and obesity-related disorders | SpringerLink
“Oleic acid affected the methylation of Pparγ and C/ebpα promoters, what correlated with higher expression. Furthermore, examined free fatty acids influenced the phenotype of mature adipocytes, especially insulin signaling pathway and adipokine secretion.”

Mitochondrial Haplogroups and Lifespan in a Population Isolate – ScienceDirect
“The lifespan-lengthening association was apparent in both sexes but only after the age of 60. Our results provide further support for the role of mitochondrial genetics in lengthening human lifespan.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1567724919301047

Calorie restriction mimetics: Can you have your cake and eat it, too? – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• We review the literature pertaining to calorie restriction mimetics (CRM).
• We discuss history, definitions, and applications of CRM.
• We discuss the concept of upstream and downstream targeting.
• We review the leading candidates for developing CRM.
• We suggest where the field is heading.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568163714001275

Effect of oral L-citrulline on brachial and aortic blood pressure defined by resting status: evidence from randomized controlled trials | SpringerLink
“L-Cit supplementation significantly decreased non-resting brachial and aortic SBP. Brachial DBP was significantly lowered by L-Cit regardless of resting status. Given the relatively small number of available trials in the stratified analyses and the potential limitations of these trials, the present findings should be interpreted cautiously and need to be confirmed in future well-designed trials with a larger sample size.”

Ketogenesis-generated β-hydroxybutyrate is an epigenetic regulator of CD8 + T-cell memory development | Nature Cell Biology
“Glycogen has long been considered to have a function in energy metabolism. However, our recent study indicated that glycogen metabolism, directed by cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase Pck1, controls the formation and maintenance of CD8+ memory T (Tmem) cells by regulating redox homeostasis1. This unusual metabolic program raises the question of how Pck1 is upregulated in CD8+ Tmem cells. Here, we show that mitochondrial acetyl coenzyme A is diverted to the ketogenesis pathway, which indirectly regulates Pck1 expression. Mechanistically, ketogenesis-derived β-hydroxybutyrate is present in CD8+ Tmem cells; β-hydroxybutyrate epigenetically modifies Lys 9 of histone H3 (H3K9) of Foxo1 and Ppargc1a (which encodes PGC-1α) with β-hydroxybutyrylation, upregulating the expression of these genes.”

Glutamine may decrease obesity-linked inflammation – Science Mission
“Glutamine could help people with obesity reduce inflammation of fat tissue and reduce fat mass, according to a new study. The researchers also show how glutamine levels can alter gene expression in several different cell types. However, more research is needed before glutamine supplementation may be recommended as a treatment for obesity. The study is published in the journal Cell Metabolism.”

Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease | NEJM
“Evidence is accumulating that eating in a 6-hour period and fasting for 18 hours can trigger a metabolic switch from glucose-based to ketone-based energy, with increased stress resistance, increased longevity, and a decreased incidence of diseases, including cancer and obesity.”

Longevity protein SIRT6 also protects against fatty liver and fatty liver disease – Science Mission
“Fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, which develops when the body produces too much fat or doesn’t metabolize fat efficiently enough, affects around 25% of the global population. Excess fat is stored in liver cells, where it accumulates and can cause fatty liver and other diseases.
In a study just published in the journal Cell Reports, researchers reveal for the first time that SIRT6, a protein involved in regulating many biological processes such as aging, obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation and metabolism, also plays a crucial role in burning and regulating liver fat metabolism.”

Age and life expectancy clocks based on machine learning analysis of mouse frailty | bioRxiv
“The identification of genes and interventions that slow or reverse aging is hampered by the lack of non-invasive metrics that can predict life expectancy of pre-clinical models. Frailty Indices (FIs) in mice are composite measures of health that are cost-effective and non-invasive, but whether they can accurately predict health and lifespan is not known. Here, mouse FIs were scored longitudinally until death and machine learning was employed to develop two clocks. ”

AMPK Activation of Flavonoids from Psidium guajava Leaves in L6 Rat Myoblast Cells and L02 Human Hepatic Cells
“The findings demonstrated that quercetin and its glycosides from Psidium guajava leaves exhibited significant AMPK activity and were likely responsible for the antidiabetic effect of Psidium guajava leaves”

Effects of sleep duration and weekend catch-up sleep on falling injury in adolescents: a population-based study – ScienceDirect
Highlights
• Insufficient sleep is well known to be an important risk factor for falls.
• The effect of weekend catch-up sleep on falls has not been studied in adolescents.
• Short sleep duration was found to be a major risk factor for falls in adolescents.
• Longer sleep duration may reduce the risk of falls among adolescents.
• Longer weekend catch-up sleep may have a protective effect against falls.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389945719316569

Antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of four different extracts derived from the roots of Nicotianatabacum L. – ScienceDirect
“In the current study we demonstrate for the first time that organic extracts derived from the roots of N. tabacum possessed antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial properties. Our data draws attention to N. tabacum as a promising source of bioactive molecules that can be utilized in pharmaceutical industry, despite the fact that tobacco smoking is a major risk factor for lung cancer.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S187638201930914X